Introduction
In the realm of veterinary medicine, precision and efficiency are paramount during surgical procedures. The quality and suitability of surgical instruments play a pivotal role in ensuring successful outcomes. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of veterinary surgical instruments, providing essential information on their types, uses, and proper care.
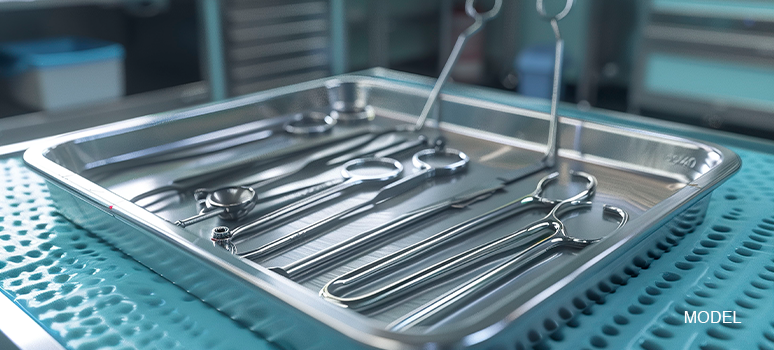
Essential Veterinary Surgical Instruments
Veterinary surgical procedures encompass a wide range of techniques, each requiring specific tools. Here are some of the most commonly used veterinary surgical instruments:
- Scalpels: These are the most basic surgical tools, used for making incisions of varying depths. They come in various blade shapes and sizes, tailored to different procedures.
- Forceps: Forceps are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues. They are available in various styles, including hemostatic forceps, tissue forceps, and dissecting forceps.
- Scissors: Scissors are essential for cutting through tissues and sutures. They are classified into several types, such as straight scissors, curved scissors, and suture scissors.
- Needle Holders: Needle holders are used to grasp and manipulate needles during suturing. They are designed with a locking mechanism to securely hold the needle in place.
- Retractors: Retractors are used to hold tissues aside during surgery, providing a clear view of the operative field. They come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the specific procedure.
- Sutures: Sutures are used to close incisions and wounds. They are available in various materials, including absorbable and non-absorbable sutures, as well as different sizes and shapes.
- Surgical Drills: Surgical drills are used for drilling holes in bones, often for the placement of screws or pins during orthopedic procedures.
- Bone Saw: Bone saws are used to cut through bones, primarily in orthopedic surgeries. They are available in various sizes and styles, including reciprocating saws and oscillating saws.
Proper Care and Maintenance
Proper care and maintenance of veterinary surgical instruments are crucial for ensuring their longevity and effectiveness. Here are some essential guidelines:
- Cleaning and Disinfection: After each use, instruments should be thoroughly cleaned to remove any organic matter. They should then be disinfected using an appropriate disinfectant solution.
- Sterilization: For invasive procedures, instruments must be sterilized to eliminate all microorganisms. Sterilization can be achieved through autoclaving or chemical sterilization.
- Storage: Instruments should be stored in a clean and dry environment, preferably in a sealed container or instrument tray.
- Regular Inspection: Instruments should be inspected regularly for signs of damage, such as corrosion, bluntness, or broken parts. Damaged instruments should be repaired or replaced promptly.
Specialty Instruments
In addition to the general-purpose instruments mentioned above, there are also specialized instruments used in various veterinary surgical fields:
- Ophthalmic Instruments: Ophthalmic surgery requires specialized instruments, such as corneal spatulas, iris hooks, and lens forceps.
- Orthopedic Instruments: Orthopedic surgery involves the use of instruments like bone saws, drill bits, and implant insertion tools.
- Soft Tissue Surgery Instruments: Soft tissue surgery often requires delicate instruments like fine-tipped forceps and microsurgical scissors.
- Endoscopic Instruments: Endoscopic procedures use specialized instruments, such as endoscopes, biopsy forceps, and snare devices.
Choosing the Right Veterinary Surgical Instruments
Selecting the appropriate veterinary surgical instruments is essential for performing successful procedures. Consider the following factors when making your choice:
- Procedure: The type of procedure will determine the specific instruments required.
- Animal Size: The size of the animal will influence the instrument size and shape.
- Instrument Quality: Invest in high-quality instruments from reputable manufacturers to ensure durability and performance.
- Ergonomics: Choose instruments that are comfortable to hold and use, reducing fatigue and the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Veterinary surgical instruments are indispensable tools for providing quality care to animals. By understanding the various types of instruments, their proper care, and the factors to consider when making selections, veterinary professionals can ensure successful surgical outcomes and optimize patient care.