Introduction: Why Accurate Dermatology Skin Scraping Matters More Than Ever
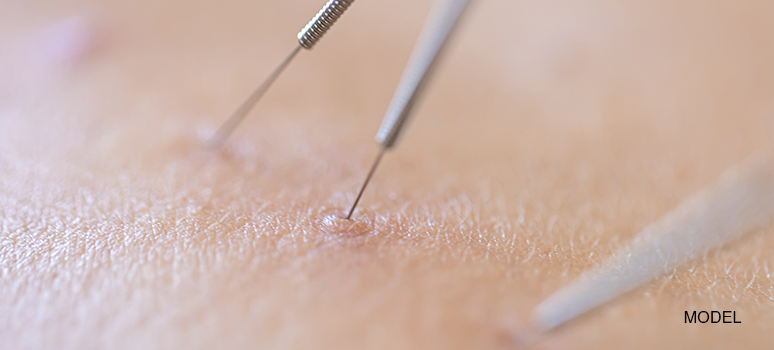
When a patient comes in with persistent itching, scaling, redness, or unexplained lesions, the question on every dermatologist’s mind is simple: What is the fastest, most reliable way to discover the real cause? This is where dermatology skin scrapping becomes a powerful diagnostic cornerstone. Despite being one of the simplest procedures in dermatology, its results can guide life-changing treatment decisions. Yet, not all clinicians perform skin scraping with the precision, technique, or tools required for accurate diagnosis.
From identifying fungal infections and scabies to confirming inflammatory skin conditions, the reliability of dermatology scraping directly influences the quality of care. With misinformation circulating online and variations in technique across training institutions, mastering top rated dermatology skin scraping is vital for consistency and accuracy.
What Is Dermatology Skin Scrapping? A Diagnostic Essential
Dermatology skin scraping is a minimally invasive clinical procedure used to collect epidermal samples for microscopic evaluation. The purpose is to identify pathogens such as:
- Dermatophytes
- Candida
- Malassezia
- Sarcoptes scabiei
- Demodex mites
- Other structural anomalies in the skin
Skin scraping plays a major role in diagnosing conditions like:
- Ringworm
- Tinea versicolor
- Scabies
- Demodicosis
- Psoriasis vs. eczema differentiation
- Keratinization disorders
Unlike biopsy, which requires anesthesia and tissue removal, dermatology scraping is fast, inexpensive, and highly effective when performed correctly. However, accuracy depends on technique and the quality of tools used.
Why Dermatology Skin Scraping Remains the Gold Standard for Fungal and Parasitic Diagnosis
Even with advanced imaging and lab technologies, skin scraping remains unmatched for detecting microscopic pathogens. Here’s why dermatologists continue to rely on it:
1. Instant Results
Most clinics can perform a KOH test or light microscopy analysis immediately after scraping. This accelerates treatment decisions.
2. Cost-Effective and Accessible
Compared to culture or PCR tests, scraping is more affordable and accessible especially in high-demand dermatology clinics.
3. High Sensitivity When Techniques Are Properly Executed
A properly collected scraping sample provides substantial evidence of fungal hyphae, mites, or eggs.
4. Minimal Discomfort to Patients
Most patients describe it as a mild scratching sensation.
5. No Need for Anesthesia
Unless the area is extremely inflamed, scraping doesn’t require numbing.
Top-rated dermatology skin scraping is precise, consistent, and highly diagnostic, especially when performed with the right instruments.
Essential Tools Needed for Top Rated Dermatology Skin Scraping
To perform successful skin scraping, dermatologists must use high-quality instruments that ensure consistent sample collection without causing unnecessary trauma. One of the industry leaders providing reliable dermatology tools is Robbins Instruments, known for precision-engineered medical instruments trusted worldwide.
Here are the essential tools you’ll need:
1. Scalpel Blade or Scraper (Size 10, 11, or 15)
The scraping blade is the most critical tool. It must be:
- Sharp enough to remove superficial epidermal layers
- Smooth enough to avoid laceration
- Angled properly for accurate collection
Clinicians often opt for disposable scalpel blades or reusable dermatology scrapers from Robbins Instruments that ensure consistency across procedures.
2. Glass Slides
High-quality slides are essential to spread and analyze samples. Clear, non-scratched slides prevent obstructed microscopic visualization.
3. Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) Solution
A 10–20% KOH solution helps dissolve keratin so the fungal elements or mites become more visible.
4. Mineral Oil (for parasite detection)
Dermatologists use mineral oil instead of KOH when scraping for:
- Scabies mites
- Demodex
- Eggs
- Fecal pellets
Mineral oil prevents specimens from scattering.
5. Microscope
A high-resolution microscope ensures accurate visualization of hyphae, spores, mites, and eggs.
6. Gloves and Alcohol Swabs
Personal protective equipment maintains hygiene and compliance with dermatology procedural standards.
How Robbins Instruments Enhances Dermatology Skin Scraping Precision
Robbins Instruments is widely trusted among dermatologists for its high-quality medical tools that deliver consistency, comfort, and reliability. Dermatology scraping requires precision, and Robbins ensures each instrument meets clinical standards.
Why choose Robbins Instruments for skin scraping?
- Razor-sharp dermatology-grade stainless steel
- Comfortable grip designs that reduce hand fatigue
- Reliable performance across hundreds of scrapes
- Disposable and reusable options
- Affordable bundles for clinics
Dermatology scraping is only as effective as the tools used and Robbins Instruments helps clinicians achieve accurate, dependable results every time.
Advanced Techniques to Improve Dermatology Skin Scraping Accuracy
Once you’ve mastered the basics, these advanced strategies can elevate your diagnostic success rate even further.
1. Warm the Skin Before Scraping
Applying a warm compress for 30 seconds softens keratin, making samples easier to collect.
2. Use Multiple Scrape Sites for Generalized Infections
Conditions like scabies or tinea corporis may require scraping from more than one location.
3. Standardize Pressure Across Scrapes
Clinics may develop internal pressure guidelines to ensure provider consistency especially useful for teaching hospitals.
4. Combine Scraping with Dermoscopy
Dermoscopy helps identify:
- Scabies burrows
- Demodex follicular openings
- Active fungal edges
This ensures scraping is performed at the most diagnostic location.
5. Use Polarized Microscopy for Fungal visualization
Enhances contrast, making hyphae easier to detect.
Conclusion: Master Dermatology Skin Scraping for Faster, More Accurate Diagnosis
Dermatology skin scraping remains the gold standard for diagnosing fungal infections, scabies, and other parasitic conditions. But accuracy doesn’t depend solely on skill, it also relies on technique, consistency, and the quality of tools used.
By following the steps, avoiding common mistakes, and using premium dermatology scraping tools from Robbins Instruments, clinicians can deliver high-precision diagnosis that improves patient outcomes and strengthens their practice’s reputation.
Whether you’re a dermatologist refining your process or a clinic aiming to offer top-rated dermatology skin scraping services, mastering this procedure will boost your confidence, diagnostic accuracy, and the overall quality of care you deliver.
FAQS
1. What conditions can dermatology skin scraping diagnose?
It is mainly used to diagnose fungal infections (like ringworm), scabies, Demodex infestation, and conditions that require microscopic evaluation of epidermal layers.
2. Does dermatology scraping hurt?
Patients usually feel mild scratching or discomfort, but pain is minimal. Anesthesia is rarely required.
3. How long does it take to get results?
Most results are available immediately under microscopy, especially for fungal hyphae and mites.
4. What tools should be used for top rated dermatology skin scraping?
High-quality blades, slides, KOH solution or mineral oil, and a microscope. For superior performance, clinicians often choose instruments from Robbins Instruments.
5. How often should dermatology scraping tools be replaced?
Disposable blades should be changed after every patient. Reusable tools must be sterilized between uses and replaced when worn down.